Exploring Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy for Wellness

Intro
In the realm of alternative therapies, vagus nerve sound therapy emerges as a fascinating point of intersection between biomedicine and holistic health practices. The vagus nerve, a complex nerve that extends from the brainstem to various organs in the body, is pivotal in regulating functions such as heart rate, digestion, and even mood stability. This therapy taps into the potential to stimulate the vagus nerve using sound, which may open up new pathways for promoting mental and physical well-being.
Research points towards a growing interest in the influence of sound on the human body, suggesting that vibrations can have profound effects on our biology. Through this article, we are set to uncover the key principles behind vagus nerve sound therapy, explore its scientific underpinning, and evaluate its practical applications.
Research Overview
The investigation into vagus nerve sound therapy begins with a concise, yet thorough, understanding of the anatomy and functionality of the vagus nerve itself. Given its extensive reach, the vagus nerve has often been linked to various health benefits, such as reducing stress responses, enhancing emotional regulation, and even influencing digestive processes. These attributes establish the foundation upon which sound therapy may build, as it aims to affect the vagus nerve in beneficial ways.
Summary of Key Findings
Recent studies suggest notable connections between sound frequencies and vagal stimulation. Sounds at specific frequencies, particularly low-frequency vibrations and certain musical tones, can facilitate physiological changes. For instance, research indicates the following:
- Increased Heart Rate Variability (HRV): Elevated HRV is often seen as a marker of resilience and adaptability of the autonomic nervous system.
- Enhanced Glymphatic System Function: Certain sound stimuli may assist in the brain's detoxification processes.
- Alleviation of Anxiety Symptoms: Many practitioners report reduced feelings of anxiety in clients who engage with sound therapy regularly.
Methodologies Employed
While the empirical study of this therapy is still in its infancy, several investigative methodologies have been utilized:
- Qualitative Interviews: Collecting personal accounts from individuals who have experienced sound therapy can provide rich insights into its impacts.
- Clinical Trials: Some studies have implemented controlled trials to observe the physiological responses to sound stimulation compared to traditional therapies.
- Case Studies: Documenting specific instances has revealed varied individual experiences and outcomes, guiding further investigations into therapeutic approaches.
By aligning sound frequencies with the body's natural rhythms, the aim is to create a harmonizing influence on mental and physical health through vagus nerve stimulation.
In-Depth Analysis
Detailed Examination of Results
One of the cornerstone findings relates directly to heart rate variability. As a higher HRV is associated with a healthy autonomic nervous system, those who engage in sound therapies often show improved scores in this area. Not only does this underscore the potential benefits, but it also raises further questions about sound's role in autonomic regulation, specifically through vagal pathways.
Moreover, the enhancement of cognitive functions through improved blood flow, energized by sound waves, beckons further inquiry into both age-related decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Comparison with Previous Studies
Prior to the exploration of sound therapy, much of the vagus nerve research focused primarily on behavioral interventions such as mindfulness and deep-breathing techniques. The lockstep with which sound therapy complements existing modalities reveals an exciting opportunity toward developing integrative practices. Collaborations between sound therapists, psychologists, and neuroscientists may lead to a more comprehensive understanding of vagal influence and mental health.
Prologue to Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy
Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy is a fascinating approach that merges the ancient wisdom of healing arts with modern scientific understanding. This therapy focuses on the vagus nerve—a pivotal component of our autonomic nervous system, responsible for regulating a wide array of bodily functions. The importance of this topic can’t be overstated; with the growing awareness of mental health issues and the quest for holistic healing methods, the exploration of sound therapy offers promising avenues for improving well-being.
The vagus nerve not only influences heart rate and digestion but also plays a significant role in emotional regulation. By tapping into its potential through sound therapy, individuals might find a unique method to manage anxiety, reduce stress, and enhance their overall mental clarity. This therapy utilizes sound frequencies that can resonate with the body, effectively stimulating the vagus nerve.
For practitioners and individuals alike, it is vital to grasp the underlying principles of Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy. Understanding its definition, scope, and historical context provides a solid foundation. Therefore, exploring these aspects will help demystify its significant role in health enhancement. This article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of the vagus nerve, how sound can affect it, and what benefits may arise from incorporating sound therapy into everyday wellness routines.
Definition and Scope
Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy is fundamentally about using sound to stimulate the vagus nerve and, by extension, support various bodily functions. This therapy often involves techniques such as music therapy, chanting, or specific sound frequencies designed to promote parasympathetic response. The scope of this therapy extends beyond traditional sound therapy; it actively seeks to harness the vibrational qualities of sound to impact health positively.
The definition leans on the understanding that sound is not merely an auditory experience but a vibration capable of penetrating the body's tissues and influencing physiological responses. By integrating this perspective, practitioners can tailor their approaches accordingly, addressing individual needs and promoting health in a personalized manner.
Historical Context
The exploration of sound as a healing tool is far from a recent development. Historically, various cultures have recognized the power of sound and vibration in facilitating healing. From the chanting of monks in ancient monasteries to the rhythmic drumming in indigenous tribes, sound has long been regarded as a conduit for emotional and spiritual healing.
In more contemporary times, researchers have begun to connect the dots between sound, the nervous system, and overall wellness. The invention of devices that generate specific frequencies has propelled this exploration further, allowing for more structured applications of sound therapy. Moreover, as mental health awareness rises, researchers and practitioners alike are reassessing the role of sound not only as an artistic expression but also as a viable therapeutic modality.
"The adoption of sound therapy in clinical settings opens doors to new horizons in health treatment, merging science and art in a powerful way."
Understanding the historical underpinnings of sound therapy enriches its present-day application, emphasizing that we stand on the shoulders of past wisdom, adapting and refining these methods to better suit our modern landscape. The intersection of history and modern science within the realm of Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy is a compelling narrative that warrants further exploration.
Understanding the Vagus Nerve
Understanding the vagus nerve is essential within the context of sound therapy and overall health because this nerve plays a pivotal role in numerous bodily functions. This extensive cranial nerve is often liken to a highway, branching off from the brain to various organs, linking the mind and body. By dissecting its significance, we can unveil a deeper understanding of how sound therapy could amplify its effects.
Anatomy of the Vagus Nerve
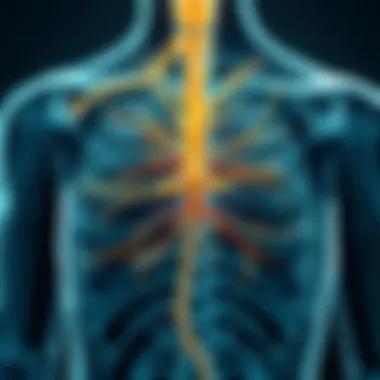
The vagus nerve, also known as cranial nerve X, is one of the longest cranial nerves in the human body. Starting from the medulla oblongata, it travels down through the neck and thorax, extending to the abdomen. The anatomy of this nerve can be likened to a tree with several branches, as it innervates many key structures, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. Its widespread reach serves as a vital communication link within the autonomic nervous system, enabling a two-way dialogue between the brain and different organ systems.
The vagus nerve consisting of motor and sensory fibers plays a role in both voluntary and involuntary functions. For instance, it is responsible for the regulation of heart rate and swallowing, while also facilitating sensations such as hunger and fullness. If we consider the complex interplay of these body functions, it becomes clear that understanding the anatomical layout of the vagus nerve is critical for grasping its implications in therapeutic practices.
Physiological Functions


The physiological functions of the vagus nerve are remarkably diverse. This nerve is the cornerstone of the parasympathetic nervous system, which is often described as the body's "rest and digest" system. It works to slow heart rate, promote digestion, and stimulate glandular secretions.
In a nutshell, the vagus nerve not only helps in calming the body but also contributes to the regulation of emotional states. Interactions between the vagus nerve and various organs have shown promising insights in how sound therapy can influence mood, anxiety, and overall well-being. Thus, acknowledging these functions is fundamental when exploring methods aimed at activating the vagus nerve through auditory means.
The Vagus Nerve and the Autonomic Nervous System
The vagus nerve's relationship with the autonomic nervous system signifies its importance in maintaining homeostasis within the body. This intricate system is divided into two main components: the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous systems. While the sympathetic system prepares the body for action—often referred to as the "fight or flight" response—the vagus nerve acts to instigate a calming effect.
Through processes such as lowering the heart rate, increasing digestive efficiency, and improving emotional regulation, the vagus nerve can be seen as a counterbalance to stress responses. Enhanced vagal tone, which refers to the activity level of the vagus nerve, is often associated with greater resilience to stress, better mental health, and improved physical well-being. Thus, harnessing sound therapy to stimulate this nerve can serve as an adjunct for individuals seeking balance in their life, underscoring the intimate connection between sound and our physiological landscape.
"The vagus nerve, often called the "wandering nerve," embodies our connection between the brain and body, emphasizing how sound can soothe and stimulate our well-being."
Understanding the vagus nerve lays the groundwork for exploring how sound therapy can act as a powerful tool to tap into the body's innate healing capabilities.
Principles of Sound Therapy
Understanding the principles behind sound therapy is crucial as it lays the groundwork for grasping how sound can influence health, particularly through the stimulation of the vagus nerve. This section seeks to demystify sound therapy, providing insight into its underlying concepts, the mechanisms that facilitate its effects, and its significant benefits. By diving into these principles, we can appreciate why sound therapy is burgeoning into a popular method for enhancing wellness.
Overview of Sound Therapy
Sound therapy revolves around the idea that auditory stimuli can promote healing by targeting various bodily systems. At its core, this therapeutic approach utilizes specific frequencies and rhythms to create an environment conducive to relaxation and balance within the body. Here are some key elements of sound therapy:
- Vibrational Healing: It is believed that sound waves can resonate with our body's own vibrations, promoting harmony and reducing stress.
- Meditative States: Many sound therapies encourage deep meditative states. This can lead to a shift from a sympathetic nervous system response (fight or flight) to a parasympathetic response (rest and digest).
- Accessibility: Sound therapy can be practiced by anyone. It doesn't require advanced training or expensive equipment, making it widely accessible.
The appeal of sound therapy lies not only in its simplicity but also in its adaptability. From using singing bowls to recorded nature sounds or even chants, individuals can tailor their experiences to their preferences.
Mechanisms of Action
Sound therapy operates through several mechanisms that engage the body and mind, creating beneficial effects on overall wellness.
Neurological Impacts
The neurological impacts of sound therapy are profound. Listening to certain frequencies stimulates brain functions, promoting neuroplasticity—the brain's ability to reorganize itself. Here are some intriguing aspects:
- Wave Patterns: Different sound frequencies can evoke various brain wave patterns, encouraging relaxation or heightened awareness, depending on the choice of sound.
- Nerve Activation: The sound can stimulate the vagus nerve directly or indirectly, which in turn helps regulate heart rates and digestion.
This makes sound therapy a valuable tool in neurological health, offering a non-invasive route to enhance brain function and emotional stability.
Psychological Effects
On the psychological front, sound therapy has been associated with improved mood regulation and emotional health. By fostering an environment of calmness, it helps mitigate anxiety and stress. Some key features include:
- Emphasis on Mindfulness: Engaging in sound therapy encourages a present-state focus, which can reduce overthinking or racing thoughts.
- Emotional Release: Many individuals report that sound can trigger cathartic emotional responses, helping them to process and release pent-up feelings.
The psychological benefits contribute significantly to its popularity as a therapeutic option, appealing to those seeking mental clarity and emotional wellbeing.
In summary, sound therapy is more than a trend; it's an evolving field grounded in meaningful interactions between sound, body, and mind. Understanding these principles not only lays the framework for its applications but also highlights how it can be a transformative practice for many.
Connection Between Sound Therapy and the Vagus Nerve
Understanding the connection between sound therapy and the vagus nerve is crucial for grasping how sound can be leveraged as a healing mechanism. This interplay can be viewed as a bridge linking the auditory signals to deep-seated physiological and emotional responses within the body. Sound therapy offers pathways to influence vagal tone, thereby impacting mental and physical well-being.
How Sound Influences Vagal Tone
Emotional Regulation
When we talk about emotional regulation, we highlight the ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences. The vagus nerve plays a pivotal role in this process, acting almost like a conductor in an orchestra, helping maintain harmony within our emotional states. Sound therapy can enhance emotional regulation by stimulating the vagus nerve, leading to improved mood and reduced anxiety.
The key characteristic here is that emotional regulation through sound offers a non-invasive, accessible method for emotional support. Many individuals find themselves overwhelmed by their feelings, a common plight in today’s fast-paced world. By harnessing sound, whether through music, chanting, or other auditory experiences, people often report a sense of calm and clarity.
One unique feature of using sound for emotional regulation is its ability to reach parts of our psyche that words often cannot. This therapeutic aspect can make sound a popular choice in therapeutic environments. However, one must consider that not all sounds may induce positive emotional responses; personal preferences play a significant role in this experience.
Physiological Responses
Turning our attention to physiological responses, this aspect embodies the body’s physical reactions to sound stimuli, influencing everything from heart rate to blood pressure. The vagus nerve, fundamentally linked to these bodily responses, helps regulate numerous autonomous functions, thus becoming central to the application of sound therapy.
The remarkable feature of physiological responses is their immediacy; people can often feel changes happening within their bodies almost instantly. For instance, soothing sound can lower blood pressure and promote relaxation, thus making sound therapy an appealing option for those grappling with stress-related health issues.
However, not all sound therapy experiences are beneficial for everyone. Some individuals may find certain sounds distressing, which can trigger adverse responses, hence the need for careful selection of sound types in therapy.
Case Studies and Anecdotal Evidence


In examining case studies and anecdotal evidence, we see how individuals have leveraged sound therapy alongside vagus nerve stimulation to improve their mental and physical health. Many health practitioners have documented positive outcomes, reflecting an emerging recognition among researchers and practitioners alike.
"Sound therapy, when combined with the principles of vagus nerve activation, holds incredible promise for enhancing holistic health."
Various individuals have shared stories of transformation—some report reduced symptoms of stress and anxiety, while others highlight improvements in chronic pain levels or even emotional well-being. Real-life examples contribute significantly to the discourse surrounding vagus nerve sound therapy and can often serve as a motivation for others seeking similar paths.
As more research unfolds, the combination of scientific findings and personal experiences will pave the way for a deeper understanding of how sound can aid in harnessing the full potential of the vagus nerve in daily practice. This burgeoning area promises not only to inform but also to inspire those looking to explore therapeutic options that reside outside conventional routes.
Applications of Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy
Understanding how Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy can be harnessed is critical for researchers and practitioners alike. This therapeutic approach opens up a range of possibilities for mental and physical health enhancement. The applications of this therapy can be categorized into two main domains: mental health benefits and physical health benefits. Each domain presents unique advantages that not only promote overall well-being but also address specific health challenges faced by individuals in today’s fast-paced world.
Mental Health Benefits
Anxiety and Stress Reduction
Addressing anxiety through sound therapy has gained traction in recent years. The integration of soothing sounds and vibrations has shown promise in helping individuals manage their anxiety symptoms effectively. The key characteristic of this approach lies in its holistic nature, as it does not rely solely on pharmaceutical interventions. Instead, it empowers individuals to engage with their own body's natural responses.
One unique feature of anxiety and stress reduction using sound therapy is its accessibility. Many techniques can be practiced at home with minimal tools, such as sound bowls or calming playlists. These simple and effective methods allow users to immediately reduce their stress levels without extensive training. The advantage here is twofold: ease of use and no side effects associated with medication, which often hampers many individuals seeking relief.
"Listening to calming sounds not only helps you feel more relaxed but actively influences your body’s physiological processes connected to the vagus nerve."
Impact on Depression
The potential impact of sound therapy on depression is another area of interest. Emerging studies indicate that engaging with sound can stimulate the vagus nerve, leading to mood improvement. This aspect characterizes sound therapy as an innovative and beneficial strategy for tackling depressive symptoms. By promoting relaxation and emotional balance, sound therapy provides a non-invasive alternative to traditional treatments.
One unique feature of this application is its adaptability to individual preferences. For example, some may find relief in music, while others may resonate more with nature sounds or guided meditation. This flexibility makes sound therapy an appealing choice for many, as it allows individuals to customize their experience to what works best for them. Additionally, the absence of significant disadvantages—in terms of accessibility and cost—makes it an attractive option for addressing depression effectively.
Physical Health Benefits
Chronic Pain Management
Chronic pain is a widespread issue that affects countless individuals, influencing their quality of life and daily activities. Sound therapy offers a possible avenue for alleviating chronic pain through its effect on the vagus nerve. The essence of this method is rooted in its ability to promote relaxation and reduce tension, which may directly contribute to decreasing pain perception.
An essential characteristic of chronic pain management via sound therapy is its dual approach: physical relaxation and psychological support. This complementary effect underscores its usefulness as a therapy. One unique aspect of this application is its relatively low cost and ease of incorporation into daily routines. For individuals struggling with chronic pain, simply incorporating calming sound sessions into their lives can lead to noticeable improvements in pain levels, without the pitfalls of invasive procedures or side effects from medications.
Inflammation and Immune Response
Another significant area where vagus nerve sound therapy is making waves is in inflammation reduction and enhancing immune responses. Studies have shown that stimulating the vagus nerve can lead to a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are critical in the body’s inflammatory processes. This benefit speaks volumes to the potential role that sound therapy could play in broader health management strategies.
The key characteristic of the relationship between sound therapy, inflammation, and immune response is the foundational role of autonomic regulation. Utilizing sound as a means to impact overall health taps into the body’s natural mechanisms for healing and recovery. A unique feature of this approach is its non-invasive nature, allowing individuals to engage in sound therapy without the need for extensive medical intervention or treatments. This opens the door for holistic health strategies that empower patients to take charge of their health in a manageable manner, leading to fewer side effects and greater satisfaction with their care.
Evidence and Research on Sound Therapy
The exploration of vagus nerve sound therapy is intrinsically tied to the scientific evidence that supports its efficacy. This section sheds light on the relevance of current studies and outlines the potential benefits while recognizing the limitations that exist within the current body of research.
Current Scientific Studies
A plethora of scientific studies have emerged, focusing on the intertwined relationship between sound therapy and vagal stimulation. Notably, recent research indicates that specific sound frequencies can effectively activate the vagus nerve, thereby enhancing its tone. Investigations led by neuroscientists have demonstrated that sounds within certain ranges may correlate with decreases in anxiety and stress levels. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine explored how low-frequency sounds significantly reduced cortisol levels, a primary stress hormone.
Moreover, a study conducted at the University of California revealed that participants exposed to therapeutic sound frequencies reported enhanced emotional stability. The findings suggest that sound therapy could be pivotal in supporting mental health by fostering emotional regulation through vagal modulation. This research simplifies complex neurological interactions, suggesting a clear connection between auditory stimuli and physiological outcomes.
The convergence of sound therapy and vagal nerve stimulation presents new horizons in the realm of holistic health and treatment options, particularly for mental and emotional well-being.
Interactions between acoustic stimuli and the vagus nerve are also under spotlight due to their implications for chronic illness management. Studies have shown that sound therapy can help mitigate symptoms related to autoimmune disorders and chronic pain conditions, giving rise to further investigations into how sound can be used as an adjunct therapy.
Limitations of Existing Research
While current studies shine a light on the potential benefits of sound therapy, it is vital to recognize that research in this area remains in its infancy. Several limitations affect the validity and applicability of findings.
- Small Sample Sizes: Many studies have been conducted with limited participant pools, which may not accurately reflect broader populations. This can skew results and hinder generalizations.
- Lack of Standardization: Variabilities in methodology—such as sound frequencies, duration of exposure, and therapeutic settings—can create inconsistencies in outcomes, making it difficult to establish universally accepted protocols.
- Short-Term Studies: Many research initiatives focus on immediate effects, failing to investigate long-term benefits or consequences. A comprehensive understanding requires longitudinal studies to assess the ongoing implications of regular sound therapy.
- Psychological Placebo Effects: The possibility that improvements in mood or physical well-being may be attributed to placebo effects remains unmeasured. This complicates the interpretation of results and the therapeutic claims made by proponents of sound therapy.
As awareness of sound therapy continues to grow, it’s crucial for researchers to address these limitations, ensuring that future studies employ rigorous, standardized methods with larger sample sizes. Fine-tuning how we measure the impact of sound on vagal tone may ultimately lead to more reliable and compelling evidence.
Practical Considerations for Implementation
In the arena of vagus nerve sound therapy, practical considerations shape how this therapy can be effectively integrated into personal health regimens. Implementing these techniques requires careful thought and a well-founded understanding of both the science behind them and the individual’s unique circumstances. This article section serves to illuminate vital aspects surrounding sound therapy, its applications, and the best practices for maximizing its benefits.
Guidelines for Practitioners
Practitioners aiming to introduce vagus nerve sound therapy should prioritize a personalized approach. Significant factors include the patient’s psychological state, physical health, and emotional well-being. It’s essential to assess individual conditions thoroughly before recommending specific sound therapies. Here are some guidelines:

- Start Slow: Begin with shorter sessions of sound therapy to allow the body to adapt, particularly if the person has never engaged with sound healing before.
- Monitor Responses: Encouraging feedback from patients is crucial. Coping mechanisms vary greatly, and immediate reactions to sound therapy can provide insight into its effectiveness for specific individuals.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Importantly, therapy should not be seen as an overnight solution. Continuous sessions can lead to more substantial benefits over time, thus managing patient expectations can contribute positively to their commitment.
"Success is often a matter of keeping faith with oneself. While sound therapy requires time, the journey itself becomes an essential part of the healing process."
Self-Application Techniques
Self-application techniques allow individuals to harness the therapeutic effects of sound without necessitating a practitioner’s presence. Empowering individuals to engage with sound therapy at home not only expands access but also fosters a greater sense of responsibility for one’s own health.
At-Home Exercises
At-home exercises serve as an empowering feature of self-application techniques. Such exercises can be simple yet effective, often integrating daily routines, which ensures that they fit effortlessly into one’s lifestyle. For example, individuals can listen to specific sound frequencies or tones while focusing on deep breathing or meditation.
Key characteristics of these exercises include:
- Accessibility: One doesn’t need special training to perform these exercises, which makes them an appealing option for anyone, regardless of background.
- Customization: At-home exercises are often tailored to fit personal preferences—some may prefer natural sounds, while others may thrive on structured tonal patterns.
The essence of these exercises lies in their ability to promote relaxation and enhance vagal tone, aiding emotional regulation and reducing physiological responses to stress. However, the potential drawback is that without guided support, individuals may misapply techniques or choose frequencies that may not harmonize effectively with their system.
Recommended Tools and Resources
The application of vagus nerve sound therapy at home can be greatly enhanced with the right tools and resources. The term tools here doesn’t refer solely to physical instruments but also to auditory resources such as apps that generate sound frequencies, or soundtracks designed for relaxation and emotional support.
A few distinguishing aspects of recommended tools include:
- User-Friendly: Most tools are designed with ease of use in mind, allowing individuals to quickly start their sound therapy journey with minimal barriers.
- Variety: With a plethora of options available—from smartphone applications to physical devices like singing bowls—individuals can experiment to find what resonates best with them.
While these tools offer various advantages, there exists the challenge of overwhelming choices that could lead to confusion or misallocation of resources. Hence, focusing on credible sources and user feedback becomes imperative in choosing the right audio tools.
Future Directions in Research
As we stand at the intersection of sound therapy and vagus nerve stimulation, it becomes increasingly apparent that further inquiry is not just beneficial—it is essential. The future of research in this area could illuminate new pathways for understanding the vagus nerve's role in holistic health and well-being. By diving deeper into the realms of sound therapy, researchers can unearth innovative methods that may enhance existing treatments for both mental and physical health issues.
Emerging Theories
In the past, the exploration of sound and its healing capabilities was met with skepticism. However, several emerging theories are gaining traction. One theory suggests a potential link between particular frequencies and their effects on the vagal response. Studies propose that specific sounds may trigger different pathways in the brain that aren’t yet fully understood. For example, the theory of entrainment, which posits that rhythmic stimuli can synchronize brainwave patterns, may explain how certain sound frequencies sooth the nervous system.
Furthermore, some researchers are exploring the placebo effect’s relationship with sound therapy, identifying that expectations of healing through sound can itself evoke physiological changes. Investigating these aspects could broaden our understanding of how intention and mental state interact with vagus nerve stimulation through sound.
Potential Areas for Expansion
Several areas remain ripe for exploration in the field of vagus nerve sound therapy. Among them:
- Technological Integration: The potential application of smartphone apps that use tailored sound frequencies to enhance vagal tone warrants deeper investigation.
- Personalized Therapy: Developing individualized sound therapy plans based on a person’s unique physiological responses may provide more effective treatment outcomes.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among neurologists, audiologists, and mental health professionals could foster comprehensive therapies that address both the mind and body more effectively.
- Broadening Research Parameters: Investigating the implications of vagus nerve stimulation through sound across various demographics and health conditions can lead to new insights.
These elements illustrate the multifaceted potential of vagus nerve sound therapy as it unfolds in the years ahead.
"The exploration into vagus nerve sound therapy is not merely academic; it holds the promise to redefine approaches to health and well-being."
To truly harness the benefits of this innovative therapy, we must encourage rigorous research, encompassing everything from basic scientific inquiry to practical applications within health systems.
Finale
In summary, the future directions in research for vagus nerve sound therapy hold a unique position in the ever-evolving landscape of health therapies. As scientific exploration continues, practitioners and patients alike can anticipate exciting developments that will strengthen the connection between sound and health.
For those interested in a deeper dive on this topic, resources such as Wikipedia, Britannica, and health forums like Reddit offer community discussions that can expand understanding and insights on the vagus nerve and sound therapies.
Finale
In summarizing the intricate relationship between the vagus nerve and sound therapy, it becomes evident that the implications of this treatment are both profound and multifaceted. This article has illuminated how engaging with sound can lead to enhanced vagal tone, ultimately fostering improved mental and physical health. Through scientific inquiries and anecdotal accounts, we’ve seen the therapeutic potential that sound holds, particularly in stress reduction, emotional regulation, and even pain management.
Summarizing Key Insights
To encapsulate the key insights detailed in this exploration:
- Vagal Nerve Functionality: The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in bridging the body and mind, significantly influencing a multitude of physiological responses and homeostasis.
- Sound Therapy Mechanisms: Various modalities in sound therapy affect the nervous system, promoting relaxation and resilience against stress.
- Evidence-Based Applications: While emerging research supports the benefits of vagus nerve sound therapy, the current understanding also highlights limitations, pointing to a need for further exploration in diverse contexts.
- Practical Applications: For practitioners and individuals alike, incorporating sound therapy techniques can enhance wellness routines, providing a gateway for personal growth and well-being.
"The mind and body are not separate. what affects one, affects the other."
This quote captures the essence of integrating sound therapy in health practices.
The Importance of Vagus Nerve Sound Therapy
The importance of vagus nerve sound therapy cannot be understated, particularly in today's high-stress environment. As more individuals seek holistic methods for improving well-being, sound therapy offers a unique, accessible tool.
Key considerations include:
- Integrative Health: Sound therapy emphasizes a holistic approach, integrating body and mind, which is crucial for comprehensive health strategies.
- Accessibility: Many sound therapy techniques can be easily practiced at home, making them approachable and cost-effective for a wide audience.
- Potential for Innovation: As research progresses, we may uncover new methodologies and technologies that enhance the efficacy and reach of vagus nerve sound therapy.
As we continue to delve into this promising field, the dialogue surrounding the benefits and methods of sound therapy will expand, fostering wider acceptance and understanding of its role in modern wellness. It is imperative for both the scientific community and the general public to remain engaged in this exploration, as the intersection of sound and health presents a frontier full of potential.















