Understanding Diabetic Photos: Types and Impact


Intro
Diabetes affects millions of people worldwide. One of its less visible yet significant aspects is the impact on visual health. Diabetic photos are a tool to capture and understand the complications arising from diabetes. This article seeks to explain these implications, the types of diabetic complications depicted, and the approaches to treatment.
Research Overview
This section explores the findings related to diabetic photos. Understanding how these images impact diagnosis and education is crucial. They serve as a bridge between clinical practice and patient comprehension.
Summary of Key Findings
Diabetic photography reveals essential information about various complications. Retinopathy, for example, is commonly documented. Retinopathy can lead to severe vision loss if not detected early. Similarly, neuropathy and foot ulcers are critical areas where photography aids in recognizing changes.
Photographs provide not only diagnostic capabilities but also assist in patient education. Patients who view these images become more aware of their condition and may take proactive steps in self-management.
Methodologies Employed
Research in this area involves various methodologies. Studies often analyze clinical images for educational purposes. These methods include comparative analysis of photographic techniques and their effectiveness in different settings. Surveys may also be conducted, gathering data from healthcare professionals about their experiences using diabetic imagery.
In-Depth Analysis
This section dives deeper into specific types of diabetic complications. It discusses how these images contribute to understanding diabetes more extensively.
Detailed Examination of Results
Each type of complication holds distinct implications. For instance, retinopathy showcases the importance of regular eye examinations. Foot ulcers reveal the need for foot care routines among diabetic patients. Photographic evidence illustrates the severity of these conditions. Regularly documented images can show progression or improvement over time, allowing for better treatment decisions.
Comparison with Previous Studies
Other studies have indicated the value of diabetic photography in education. For example, research from the American Diabetes Association emphasizes the role of visual aids in understanding health conditions. By comparing these findings, we can appreciate the advancement in treatment protocols and patient education techniques.
"Visual documentation through diabetic photos not only aids in diagnosis but also transforms patient engagement in their own healthcare."
In summary, the holistic view of diabetic photos presents a clear narrative. It highlights their significance in both clinical practice and education, providing vital insights for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Intro to Diabetic Photo
Diabetic photography plays a pivotal role in the management of diabetes. This practice not only aids clinicians in diagnosing complications but also empowers patients through visual documentation of their condition. As diabetes persists, its physical manifestations can have profound implications for a patient's health and quality of life. The ability to visually capture these changes can enhance understanding and streamline treatment approaches.
Defining Diabetic Photos
Diabetic photos are images captured to document various complications that arise from diabetes. The most prominent types include photographs of the retina, which reveal diabetic retinopathy, images that illustrate diabetic foot ulcers, and pictures that depict signs of diabetic neuropathy. Each of these categories has specific indications, helping healthcare professionals assess the severity of complications and determine the most appropriate interventions. The usefulness of this practice is underscored by its ability to create a permanent visual record, which can be referenced over time.
Purpose of Diabetic Imaging
The primary purpose of diabetic imaging is to provide insight into the health status of patients with diabetes. These images serve several key functions:
- Diagnosis: Clinicians rely on diabetic photos as essential tools for diagnosing conditions like retinopathy and neuropathy.
- Monitoring: Regular imaging helps track the progression of diabetic complications over time, allowing for timely adjustments in treatment plans.
- Patient Education: Sharing these images with patients enhances their understanding of their condition, thus encouraging better self-management.
- Research: Diabetic photos contribute to ongoing studies, helping to identify trends and develop more effective strategies for diabetes management.
The use of diabetic photography can significantly enhance patient engagement and improve treatment outcomes.
In summary, the importance of diabetic photography cannot be overstated. By providing visual evidence of diabetes-related complications, these images catalyze a more informed approach to both diagnosis and management.
Types of Diabetic Complications Documented through Photos
The documentation of diabetic complications through photography offers invaluable insights into the management and understanding of diabetes. This approach allows for a visual account of various consequences that can arise due to poor regulation of blood glucose levels. Through images, healthcare professionals can analyze the severity of complications and tailor treatments accordingly. It also encourages better communication between patients and providers, as visuals often tell a story more effectively than words.
Different diabetic complications manifest in distinctive ways, which can be identified through careful imaging. Such documentation aids in tracking disease progression and can facilitate early interventions. This aspect is crucial as it can prevent more severe complications and improve patient outcomes.
In this article, we will discuss three primary types of complications often depicted in diabetic photography:


- Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diabetic Neuropathy
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Each of these complications has unique characteristics and implications that merit detailed exploration.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness among adults. The condition arises from damage to the blood vessels in the retina, often caused by extended periods of high blood sugar. Images capturing the retina can show early changes like dot-and-blot hemorrhages, cotton wool spots, and exudates. These visual markers enable early diagnosis and prompt intervention, which are vital for preserving vision.
Furthermore, imaging technologies such as fundus photography and optical coherence tomography allow for detailed examinations of the retina, providing clarity on the condition's severity. By documenting these changes, healthcare professionals can monitor a patient's response to treatment and make necessary adjustments.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a group of nerve disorders caused by diabetes. This complication can affect various parts of the body, including the feet and hands. Photography acts as an essential tool to document physical manifestations such as skin changes or ulcerations that arise due to nerve damage.
Capturing images of diabetic neuropathy can assist in diagnosing the extent of nerve impairment and guide the management of symptoms. For instance, visual evidence of foot deformities or injury helps healthcare providers create comprehensive care plans, emphasizing the need for preventive measures, like proper footwear and daily foot inspections.
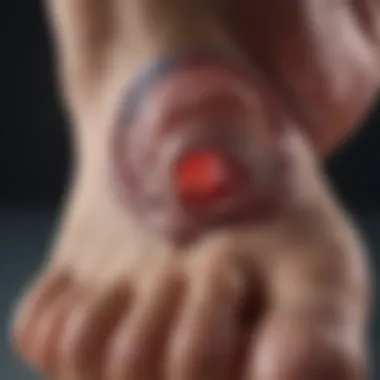
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers represent a serious risk for individuals with diabetes. The condition occurs due to a combination of neuropathy and poor circulation, leading to skin breakdown and potential infections. Photographic documentation is critical in assessing the size, depth, and condition of ulcers.
By capturing regular images of foot ulcers, healthcare providers can measure healing progress or identify complications like infections or necrosis. This information becomes vital in deciding the appropriate treatment, whether it be wound care, medication, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. The role of photography in managing diabetic foot ulcers cannot be overstated; it enhances patient monitoring and contributes to better outcomes.
"Regular documentation through photography not only assists in clinical assessments but also reinforces the importance of patient education around self-care measures."
In summary, diabetic photography is indispensable across various complications, offering visual insights that inform diagnosis, treatment, and patient education. Understanding the implications associated with retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot ulcers empowers both healthcare providers and patients to navigate diabetes with informed strategies.
The Importance of Imaging in Diagnosis
Imaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of diabetic complications, offering detailed visual insights that can significantly impact patient care. As diabetes progresses, various complications may arise that can be subtle and difficult to detect without proper imaging techniques. Utilizing diabetic photos enables healthcare professionals to observe and analyze changes in patient conditions more effectively.
The benefits of imaging in diagnosis are numerous. First, it provides a visual representation of the severity of complications such as diabetic retinopathy and neuropathy. This can lead to more informed decision-making regarding the best course of treatment. Second, imaging aids in documenting the progression of these conditions over time. Medical history and patient symptoms can sometimes lead to ambiguity; however, visual documentation can help clarify the situation.
Furthermore, imaging facilitates better communication between healthcare providers and patients. It allows for discussions that are grounded in observable data rather than subjective experience alone. Patients can see their conditions visually, which can enhance their understanding and engagement in their treatment plans.
Visual Indicators of Complications
Visual indicators are vital in identifying potential complications associated with diabetes. For instance, changes in retinal images can indicate diabetic retinopathy, characterized by abnormalities such as microaneurysms, hemorrhages, and retinal edema. By capturing these indicators through photographic methods, clinicians can swiftly assess the damage from these complications.
Another example is diabetic foot ulcers. Imaging can reveal skin and tissue changes that typically do not have clear signs in the early stages. Healthcare providers may identify discoloration, swelling, or signs of infection via photographs, leading to timely interventions that prevent further deterioration.
"Imaging not only captures the present state but also provides a comparison for future examinations."
Using Photos for Early Detection
Early detection of diabetic complications is essential to manage the condition effectively. The integration of photos into regular screenings offers a proactive approach to diabetes care. By employing imaging tools, clinicians can detect minor changes that might go unnoticed during standard examinations.
For example, high-resolution images of the retina taken at regular intervals can reveal gradual changes that signal the early stages of retinopathy. These changes may not be noticeable through other diagnostic methods until they have progressed significantly. In neurological assessments, images of the feet can uncover early signs of neuropathy, such as loss of sensations or unexplained bruising.
Moreover, the availability of mobile applications for diabetes management further enhances the prospects of early detection. Patients can document their condition regularly, providing healthcare providers with a rich archive of visual information, all of which can be analyzed for patterns and signs that warrant closer observation or intervention.
Technological Advances in Diabetic Photography
Technological advancements have transformed the field of diabetic photography. The integration of innovative imaging techniques directly assists in the diagnosis and management of diabetes-related complications. This section explores two main components of these advancements: digital imaging techniques and mobile applications.
Digital Imaging Techniques
Digital imaging has introduced a new era in the assessment of diabetic patients. High-resolution cameras, combined with advanced software, can now capture the fine details necessary for accurate diagnosis.
The use of retinal cameras, for instance, enables the visualization of the retina with precision. These cameras can identify early-stage diabetic retinopathy by highlighting subtle changes in the blood vessels of the retina. Moreover, image processing algorithms are deployed to help detect abnormalities. These algorithms can enhance images, allowing healthcare professionals to analyze important features easily. Some advantages of digital imaging techniques include:
- Enhanced accuracy in detecting complications like retinopathy.
- Improved accessibility for rural or underserved populations, where distance to healthcare facilities is a barrier.
- Speedy results, significantly reducing the time from examination to diagnosis, which is crucial in managing diabetes effectively.

In addition, the digital storage of images allows for longitudinal studies, enhancing the understanding of how diabetic complications evolve over time. By comparing images taken over years, doctors can better tailor treatment interventions.
Mobile Applications for Diabetes Management
Mobile technology has also transformed diabetes management significantly. There is a growing number of mobile applications designed with users in focus. These apps often contain features like photo logging, which allow patients to document their symptoms and track health changes visually.
Some popular applications include MySugr and Glucose Buddy. They offer functionalities such as:
- Photo capture for daily records of conditions like foot ulcers, which helps document changes over time.
- Reminders for medication and appointments, assisting individuals in adhering to treatment plans.
- Data sharing options, allowing users to send their progress reports and photos to healthcare providers, facilitating informed discussions during consultations.
Despite the benefits, there are considerations that must be taken into account, including potential data privacy issues and the need for user education to maximize these tools effectively.
Educational Uses of Diabetic Photography
Diabetic photography serves a critical role in both clinical and educational contexts. By visually documenting diabetes-related complications, healthcare professionals and patients gain valuable insights that enhance understanding and improve decision-making. This section discusses how diabetic photography benefits healthcare training and raises patient awareness.
Training Healthcare Professionals
The integration of diabetic photographs in the training of healthcare professionals cannot be overstated. These visuals provide real-life examples of diabetic complications, such as diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot ulcers. Medical students and residents can study these images to understand symptomatology and progression of the diseases.
Importance of Visual Learning
Visuals often facilitate quicker comprehension. When medical trainees view images of various diabetic conditions, they can better appreciate variations in presentation and severity. This experience fosters a deeper understanding, which textual descriptions alone might not impart.
Another significant aspect is the application of diagnostic skills.
Professionals learn to identify signs of complications through the photographs. They become adept at discerning subtle changes that may indicate a need for intervention. The training process thus shifts to active engagement rather than passive reading.
Key Elements in Professional Training
- Case Studies: Using photographic case studies for discussions can bridge clinical theory and practice.
- Feedback Mechanism: Photographs support practical evaluations. Peers and mentors provide feedback on image interpretations, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
- Standardization: The use of standardized photographs aids in establishing benchmarks for diagnoses.
"Visual aids in medical training provide a shortcut to understanding complex concepts, making education more effective."
Patient Education and Awareness
Diabetic photography also has significant implications for patient education. It empowers individuals to take control of their health by increasing awareness of potential complications. By illustrating the serious consequences of uncontrolled diabetes, images can motivate patients to adhere to treatment plans.
The emotional impact of these images is profound. Patients seeing real-life examples of diabetic complications may feel a sense of urgency regarding their health. Educational resources that incorporate diabetic photographs can lead to informed conversations between patients and healthcare providers.
Benefits of Patient Education through Photography
- Increased Awareness: Images can help patients recognize early signs of complications.
- Treatment Adherence: When patients understand the risks associated with poor glucose control, they may be more likely to follow medical advice.
- Self-Monitoring: By educating patients about what to look for, they can engage in self-care practices that may prevent severe complications.
Lastly, diabetic photographs utilized in educational materials can help demystify the condition. By presenting diabetes not just as a medical diagnosis but as a condition that can visually manifest in various ways, patients may feel more connected and involved in their treatment pathways.
Emotional Impact of Diabetes Captured through Photos
The emotional weight of living with diabetes is profound, and capturing these feelings through photographs serves various important functions. Photos provide a window into patient lives, illustrating struggles and triumphs in a visually impactful manner. Understanding this emotional aspect is crucial for healthcare professionals, patients, and educators alike.
Diabetes can often feel isolating, and photography serves as a tool to bridge the gap between patient experiences and public understanding. Emotional images can humanize complex medical conditions, allowing viewers to grasp the psychological and emotional realities faced by diabetes patients. Furthermore, these images can create a sense of community and shared experience among individuals dealing with similar challenges.
Understanding Patient Experiences
Diabetes affects each patient differently, and photography can encapsulate a range of experiences. By documenting daily life, individuals can share their personal stories about diabetes. This visual documentation may include everything from managing daily injections to the emotional struggles associated with blood sugar fluctuations.
A photograph can express feelings that words might not fully capture. For example, an image showing a patient preparing a meal with careful consideration of their diet can communicate diligence and caution. Similarly, an image depicting a moment of frustration after an unexpected spike in blood sugar levels conveys the emotional toil of managing the condition.
In addition, these patient experiences showcased in photos can serve as learning tools for healthcare providers. Understanding the emotional context behind a patient's journey can enhance the ability of medical professionals to deliver empathy-led care.
The Role of Images in Emotional Healing
Images play a notable role in emotional healing for diabetes patients. They can act as therapeutic instruments, helping individuals process their feelings regarding their diagnosis and ongoing management. For some, photography allows one to document their journey toward acceptance and understanding of their condition.

Moreover, expressive photography can also foster hope. Photos that depict positive aspects of living with diabetes, such as community engagement, advocacy and successful management strategies offer encouragement to others who feel lost or overwhelmed. This is essential because hope* can lead to improved adherence to treatment and willingness to confront the challenges posed by diabetes.
When patients see themselves reflected positively in images, it can improve self-esteem and reduce feelings of stigma. Additionally, sharing these images on social platforms can open dialogues and support networks, further enhancing emotional well-being. As individuals connect through shared visuals, they can realize they are not alone in their challenges, thus paving the way for emotional healing and resilience.
"Visual narratives in medicine are not merely about medical conditions; they are integral to understanding the holistic experience of patients."
By utilizing photography, healthcare professionals and educators can cultivate a greater understanding of diabetes, which extends beyond mere clinical management to encompass emotional and psychological healing as well.
Challenges and Limitations of Diabetic Photography
In the realm of diabetic photography, there are numerous obstacles that hinder optimal outcomes. Understanding these challenges is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. While the advantages of diabetic imaging are apparent, it is equally essential to acknowledge the limitations that can affect diagnosis, treatment efficacy, and patient education. Addressing these challenges can help in enhancing the overall utility of diabetic photography in clinical practice.
Quality and Accessibility Issues
Quality is paramount in any medical imaging practice. Poor-quality images can lead to misinterpretations and missed diagnoses. In the context of diabetic photography, several factors contribute to quality concerns.
- Device Limitations: Not all imaging devices offer the same level of accuracy. Some may not have the necessary resolution to capture fine details typical of diabetic complications.
- User Skills: The competence of the individual capturing the images plays a significant role. Proper techniques and expertise are required for clear and effective documentation.
- Environmental Conditions: Factors such as lighting and background can influence the clarity of the photographs taken in different settings, whether clinical or home-based.
- Patient Factors: Some patients may have difficulty cooperating during imaging due to discomfort or anxiety, affecting the final output.
Accessibility is another critical consideration. Not all patients have equal access to advanced imaging technology. This disparity can occur due to geographical barriers or financial constraints.
"Eliminating quality and accessibility issues is vital for effective use of diabetic photography in improving patient outcomes."
Interpreting Images Accurately
The ability to interpret images accurately is fundamental to the diagnostic value of diabetic photography. Misinterpretation can lead to incorrect treatment plans, adversely affecting health outcomes. Factors contributing to interpretation challenges include:
- Variability in Image Quality: Images from different devices or settings may vary considerably, making it hard to standardize interpretations.
- Training and Knowledge: Not all healthcare providers receive extensive training in reading diabetic photographs. This gap can lead to inconsistencies in diagnosis.
- Image Overload: In settings where numerous images are collected, the sheer volume can overwhelm healthcare professionals, leading to important details being overlooked.
- Annotation and Context: Without proper context or annotations, interpreting the significance of an image can be challenging. Each photograph needs to be part of a larger narrative for accurate assessment.
Addressing both quality and interpretation issues is essential. Improving these facets can enhance the value of diabetic photography in managing diabetes and its complications significantly.
Future Directions in Diabetic Imaging
The exploration of future directions in diabetic imaging holds significant relevance in evolving methodologies for managing diabetes. This topic encompasses advancements that could improve diagnosis, treatment, and patient education. The incorporation of innovative technologies offers several potential benefits, such as enhancing the accuracy of diagnoses, enabling timely interventions, and fostering a more interactive relationship between patients and healthcare providers. Addressing challenges in this area will be crucial for making diabetic photography even more effective.
Innovations on the Horizon
Innovative technologies are reshaping the landscape of diabetic imaging. One key area includes the development of more sophisticated cameras and imaging devices capable of capturing high-quality images. These images can help in identifying pathological changes with greater precision. Furthermore, portable and affordable diagnostic tools are becoming increasingly available.
- Telemedicine: This is crucial for remote consultations, especially in areas lacking expert healthcare providers. Patients can share images with specialists, receiving feedback without travel.
- Advanced Image Processing: The application of advanced algorithms to enhance image quality is another exciting frontier. Improved features may assist in better visualizing diabetic complications.
- Wearable Technology: Devices that continuously monitor glucose levels and physiological changes may soon integrate imaging capabilities. This integration can provide real-time data alongside visual documentation, giving a comprehensive picture of a patient's condition.
Integrating AI in Diabetic Photography
The integration of artificial intelligence in diabetic photography presents an important evolution in managing diabetic complications. AI can process vast amounts of data quickly. This capability enables more accurate interpretations of diabetic images. AI systems can learn from existing datasets and identify patterns not readily visible to human eyes.
- Automated Identification: AI algorithms can automatically detect signs of complications like retinopathy or neuropathy, leading to earlier interventions.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data, AI can forecast potential complications. This predictive capability can guide both patients and clinicians in proactive management strategies.
- Streamlining Workflow: AI can significantly reduce the time medical professionals spend interpreting images. This efficiency allows them to focus more on patient care and approach treatment decisions based on accurate interpretations.
In the future, the combination of innovations and AI integration might not only enhance outcomes but also reinforce patient empowerment in managing their diabetic journey.
In summary, the future of diabetic imaging is promising. Emerging technologies and artificial intelligence are positioned to transform the field, ultimately improving the standard of care for individuals living with diabetes.
Closure
The conclusion of this article synthesizes crucial insights surrounding diabetic photos, emphasizing their multi-faceted role in the realm of diabetes management. Understanding the implications of diabetic imagery not only highlights the types of complications but also showcases the applications in diagnosis and education.
Summarizing Key Findings
Diabetic photos serve as a vital tool for both healthcare providers and patients. They provide visual evidence of conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and foot ulcers. These images enable early detection and intervention, which can dramatically impact patient outcomes. The advancements in digital imaging technology also enhance the quality and accessibility of these photographs, making them integral in today’s medical practices.
"Visual representation of diabetic conditions can lead to timely interventions and improved patient education."
Furthermore, the emotional impact of these visuals cannot be overstated. They help convey experiences and foster understanding between medical professionals and patients. Therefore, diabetic photos are not merely illustrative; they transform the management of diabetes into a more person-centered approach, ultimately facilitating better care.
Encouraging Continued Research
Despite the progress seen in diabetic photography, the need for continued research remains critical. Innovations in imaging technology and the integration of artificial intelligence offer numerous avenues for exploration. Research can enhance the accuracy of image interpretation, helping to bridge gaps in knowledge concerning diabetic complications. Future studies should also focus on patient engagement strategies, utilizing diabetic photos as educational resources.
By investing in ongoing exploration, the field can adapt and emerge with innovative methods to enhance both patient outcomes and understanding of diabetes. The dialogue between technology and healthcare must continue to evolve so that diabetic imaging adapts to meet the future challenges of chronic disease management.















