Understanding Autosomal Polycystic Kidney Disease


Intro
Autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is a significant health concern that can affect many individuals worldwide. The genetic nature of this disorder leads to the development of cysts in the kidneys. Understanding APKD is crucial as it presents both clinical challenges and implications for healthcare systems. This article delves into crucial aspects of APKD, providing insights into its genetic foundations, clinical manifestations, and management strategies related to the disease.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Research has shown that APKD primarily stems from mutations in two genes: PKD1 and PKD2. These mutations lead to varying severity of the disease, with PKD1 mutations often resulting in a more aggressive form. Patients may experience hypertension, abdominal pain, and kidney failure as primary complications.
Methodologies Employed
Studies on APKD have utilized a range of methodologies, including genetic testing, imaging techniques, and renal function assessments. Genetic tests, such as sequencing of the PKD1 and PKD2 genes, are essential to confirm a diagnosis. Imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI play a vital role in visualizing cystic changes in the kidneys and monitoring disease progression. Furthermore, clinical trials are conducted to assess the efficacy of various treatment strategies.
In-Depth Analysis
Detailed Examination of Results
Different studies have revealed a wide array of clinical symptoms associated with APKD. While some patients remain asymptomatic for years, others may display early signs indicating rapid disease progression. This heterogeneity makes it vital to adopt personalized monitoring approaches for individuals diagnosed with APKD.
Comparison with Previous Studies
Recent findings have drawn comparisons to historical data on APKD, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and management. While past strategies focused predominantly on symptomatic relief, cutting-edge research is now honing in on targeted therapies that address the root genetic causes of the disease. This evolution in research direction suggests a promising future for APKD management.
"Autosomal polycystic kidney disease is not just a genetic disorder; it represents a spectrum of clinical challenges that vary widely among affected individuals. Understanding this variability is key to effective management."
Closure
In summary, understanding the complexities of autosomal polycystic kidney disease and the ongoing research provides valuable perspectives for healthcare professionals and researchers alike. By combining genetic insights with clinical approaches, the management of APKD can improve, leading to better outcomes for those affected by this challenging disorder.
Prelude to Autosomal Polycystic Kidney Disease
Autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is a complex genetic disorder with significant implications for patients and healthcare systems. The importance of understanding this condition lies not only in recognizing its symptoms and manifestations but also in grasping its genetic basis and treatment options. This section introduces the key components necessary for a comprehensive overview.
APKD primarily affects the kidneys, leading to the formation of cysts that disrupt normal kidney function. As these cysts grow, they can cause a range of complications, significantly impairing renal health. Understanding APKD is essential for early diagnosis and management, which ultimately affects patient outcomes.
Additionally, the broader impact of APKD extends to familial, psychological, and economic dimensions. It is vital for students, researchers, educators, and healthcare professionals to grasp the interconnectedness of genetics, clinical presentation, and management strategies. The following subsections delve deeper into the definition, prevalence, and historical context of APKD.
Definition of APKD
Autosomal polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder characterized by the development of numerous cysts in the kidneys. These cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can grow large and lead to further complications like high blood pressure and eventual kidney failure. APKD generally manifests as two forms: APKD type 1 and APKD type 2, which differ based on the location of the responsible genetic mutations. Understanding the definition of APKD is foundational for recognizing its effects and for early intervention.
Epidemiology and Prevalence
The prevalence of APKD varies across populations but is substantially recognized as one of the most common hereditary kidney diseases. Approximately 1 in 400 to 1 in 1,000 individuals are affected. Understanding the epidemiology helps in identifying at-risk populations and crafting public health strategies. The disease occurs equally in males and females, but the progression may differ depending on genetic factors.
Historical Context
The historical context of APKD reveals its longstanding recognition in medical literature. The genetic basis of the disease was initially described in the mid-20th century, when researchers identified its pattern of inheritance. Over time, advancements in genetic research have elucidated the specific mutations associated with APKD. As a result, the understanding of the disease has evolved, leading to improved diagnostic tools and treatment strategies.
"Understanding the historical developments of a disease can often provide insight into current treatment protocols and research focuses."
Genetic Basis of APKD
The genetic basis of autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is fundamental to understanding its pathogenesis and clinical management. This section will elucidate the specific mutations and inheritance patterns associated with APKD, as well as focus on the pivotal roles of the PKD1 and PKD2 genes. Grasping these genetic elements is crucial for healthcare professionals and researchers, as it can guide diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, informing patient counseling and further research developments.
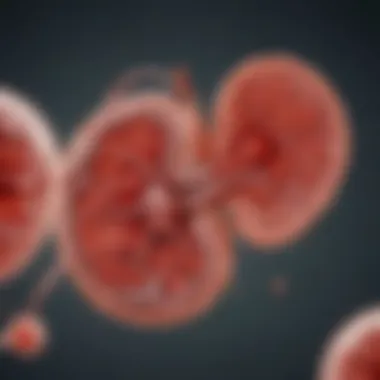

Genetic Mutations Involved
Autosomal polycystic kidney disease primarily arises from mutations in two key genes: PKD1 and PKD2. FKJD mutations in the PKD1 gene, which is located on chromosome 16, are responsible for the more severe form of the disease, generally presenting in early adulthood. Conversely, mutations in the PKD2 gene on chromosome 4 tend to result in a milder phenotype, with symptoms typically emerging later in life.
Research indicates that about 85% of APKD cases are linked to PKD1 mutations, while PKD2 mutations account for the remaining 15%. The varying severity of kidney disease associated with these mutations is linked to the specific biological functions of the proteins produced by the PKD genes. Understanding these genetic mutations can help in the development of targeted therapies aimed at halting disease progression.
Inheritance Patterns
The inheritance pattern of autosomal polycystic kidney disease is autosomal dominant, meaning only a single copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can result in the disease. This characteristic leads to a 50% risk of passing the mutation to offspring. Because of this dominant inheritance, APKD can arise in families with no prior history of the condition, often appearing as a new mutation. Examination of familial patterns is vital, as it can influence clinical decisions and genetic counseling for affected individuals and their families.
Role of PKD1 and PKD2 Genes
The PKD1 and PKD2 genes encode proteins that are integral to kidney function. The protein produced by PKD1, polycystin-1, plays a significant role in kidney tubule cell growth and differentiation, while polycystin-2, encoded by PKD2, is involved in calcium signaling and tubular fluid homeostasis. Mutations in these genes disrupt normal renal architecture, leading to cyst formation.
Furthermore, the interaction between polycystin-1 and polycystin-2 is critical for maintaining normal renal function. Disruption of this interaction can result in heightened cellular proliferation, cyst expansion, and ultimately renal failure. As research continues, the exploration of these genes' functions expands, revealing potential therapeutic targets for managing APKD more effectively in the future.
The understanding of the genetic basis of autosomal polycystic kidney disease is evolving, offering hope for more effective clinical interventions and improved patient outcomes.
In summary, the genetic basis of APKD encompasses specific mutations, inheritance patterns, and the essential roles played by PKD1 and PKD2 genes. Clarifying this information contributes significantly to research, diagnosis, and patient care surrounding this complex genetic disorder. By recognizing these factors, professionals can gain insights into potential therapeutic avenues, ultimately improving the quality of life for those affected by APKD.
Clinical Manifestations of APKD
Understanding the clinical manifestations of autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is essential for comprehending its overall impact on patients. These manifestations inform not only the diagnosis but also the progression and management of the disease. Clinical symptoms can significantly affect a patient's quality of life and influence treatment decisions. It is crucial for healthcare providers to recognize these manifestations early, as timely interventions can potentially mitigate some complications associated with the disease.
Renal Complications
The renal complications associated with APKD are well-documented and form a core aspect of the disease. As cysts form in the kidneys, they can increase in size and number over time, leading to various complications. The most common renal issues include:
- Hypertension: Patients often experience high blood pressure due to increased renal vascular resistance.
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD): The progressive loss of renal function can occur in late stages, eventually leading to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Cyst infections: Infections within renal cysts can cause pain and febrile reactions.
- Kidney stones: Patients with APKD are at higher risk of developing kidney stones.
"The emergence of renal complications is a defining characteristic of APKD, often influencing long-term prognosis and patient management."
These complications require vigilant monitoring, including regular imaging studies and assessments of renal function. Understanding these risks helps in developing tailored treatment plans and in educating patients regarding symptom management.
Extrarenal Manifestations
While renal complications dominate the clinical picture of APKD, extrarenal manifestations also play a critical role in patient experience. These manifestations can affect various systems in the body, including:
- Liver cysts: Many patients will develop hepatic cysts, which may remain asymptomatic but can lead to complications such as infection.
- Pancreatic cysts: Similar to hepatic cysts, these may also occur without symptoms but can affect function in severe cases.
- Cardiovascular issues: There is an increased incidence of heart valve abnormalities and increased cardiovascular risk among individuals with APKD.
- Diverticular disease: Patients may exhibit a higher prevalence of diverticula in the gastrointestinal tract.
Recognizing these extrarenal manifestations is vital as they can complicate management strategies and contribute to the overall burden of disease.
Symptomatology Progression
The symptomatology of APKD typically progresses through distinct stages that correlate with the evolution of renal cysts and overall kidney function. Early stages may present few symptoms, often going unnoticed. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms become more apparent and can include:
- Back or flank pain
- Abdominal fullness or distension
- Nausea or vomiting during cysts growing
- Frequent urination
The rate of progression varies greatly among individuals, influenced by genetic factors and the presence of other health conditions.
Early intervention based on recognizing the symptoms may enhance the patient’s management strategy and ultimately improve quality of life. Monitoring disease progression is necessary for adapting treatment approaches and maximizing therapeutic outcomes.
Diagnosis of APKD
Accurate diagnosis of Autosomal Polycystic Kidney Disease (APKD) is crucial for effective management and treatment. The importance of timely diagnosis cannot be understated, as it allows for early intervention, which can delay or even prevent the onset of severe kidney complications. When APKD is diagnosed early, affected individuals can work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their condition and initiate lifestyle changes or treatments to maintain kidney function. This section will explore the diagnostic criteria, imaging techniques, and genetic testing considerations involved in diagnosing APKD.
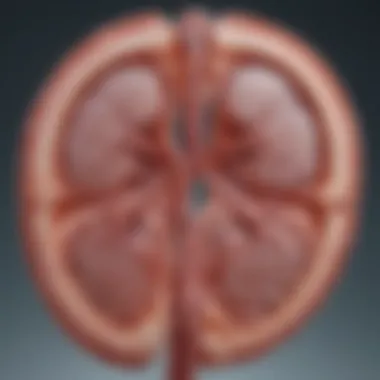

Diagnostic Criteria
Diagnosis of APKD generally follows established clinical and genetic guidelines. The primary criteria often hinge on the identification of renal cysts through imaging studies. According to the modified Ravine criteria:
- Adults: The presence of two or more cysts in each kidney is indicative of APKD. Further, if there is a family history, diagnosis can occur with fewer cysts.
- Children: Similar diagnostic benchmarks apply, though cysts may be fewer in number. Genetic tests may play a larger role in pediatric cases.
Recognition of the associated symptoms, such as hypertension and hematuria, also contributes significantly to the diagnosis. This multidimensional approach ensures a comprehensive and accurate assessment of the patient’s condition.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging serves as a central pillar for diagnosing APKD. Various techniques are used, with the most common being ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI:
- Ultrasound: This is the first-line imaging modality due to its availability and non-invasive nature. It can effectively visualize renal cysts and assess kidney size.
- CT scans: If ultrasound results are inconclusive, a CT scan can provide detailed cross-sectional imaging of the kidneys and surrounding tissues. It offers a more definitive assessment of cyst size and location.
- MRI: This is appreciated for its ability to offer high-resolution images without radiation exposure. It's particularly useful in complex cases or when other imaging shows atypical findings.
Each imaging technique has its own merits, and the choice often depends on the patient’s specific situation and potential comorbidities.
Genetic Testing Considerations
Genetic testing provides an additional layer of analysis for confirming a diagnosis of APKD. It is particularly valuable in instances where clinical and imaging findings are insufficient or ambiguous. Testing for mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes is a core component in this context. Some considerations include:
- Timing: Genetic testing is most useful when the diagnosis is unclear or when there's a strong family history of the disease.
- Counseling: Pre- and post-test genetic counseling should be offered to individuals considering testing. This helps them understand the implications of results and manage expectations.
- Family Testing: If an individual is diagnosed, it can be beneficial to test family members for early identification of at-risk individuals.
Genetic testing can provide clarity regarding the inheritance pattern and risk assessment for family members, thereby shaping future healthcare decisions.
In summary, the diagnosis of APKD is a comprehensive process that involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging techniques, and genetic testing. This multifaceted approach not only facilitates early detection but also helps in planning a management strategy tailored to the individual's needs.
Management and Treatment Strategies
The topic of management and treatment strategies for autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is crucial in addressing the complexities of this condition. Effective management can greatly influence the progression of the disease and enhance the quality of life for those affected. It is essential to understand that APKD can lead to serious complications, including end-stage renal disease. Therefore, developing a comprehensive approach to management is vital. Various strategies exist, ranging from conservative management to pharmacological and surgical interventions, each with unique benefits and considerations.
Conservative Management
Conservative management involves lifestyle modifications and monitoring to slow the progression of kidney disease. Key aspects of this approach include:
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups and monitoring kidney function are essential. This can help catch complications early.
- Dietary Modifications: A balanced diet low in sodium can help manage blood pressure. Staying hydrated is crucial as well.
- Control of Blood Pressure: Maintaining optimal blood pressure levels, often through lifestyle changes, is critical because hypertension is common in APKD patients.
- Physical Activity: Exercise can promote overall health and help maintain a healthy weight, reducing the burden on the kidneys.
This approach allows patients to take an active role in their health management, reducing complications and improving their overall well-being.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments for APKD focus on managing symptoms and complications. Some common medication categories include:
- Antihypertensives: Medications such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) can help control blood pressure and may slow kidney function decline.
- Pain Management: While not directly affecting kidney function, pain management is important due to potential pain from cysts.
- Preventing Infections: Antibiotics may be necessary if urinary or kidney infections occur, as these can be more common in individuals with APKD.
- Clinical Trials: New medications are continually being researched, such as tolvaptan, which has shown promise in slowing disease progression in some patients.
Tailoring pharmacological treatments to individual patient needs can optimize control of symptoms and enhance life quality.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical interventions may become necessary as the disease progresses, particularly when complications arise. Some key surgical options include:
- Cystectomy: In cases of particularly large or painful cysts, surgical removal can provide relief and improve kidney function.
- Nephrectomy: This procedure involves the removal of one or both kidneys, typically done in patients transitioning to dialysis or kidney transplantation.
- Dialysis: For individuals experiencing kidney failure, dialysis becomes crucial. Two main types of dialysis are hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Each has a different approach and suitability depending on the patient's condition.
Surgical options often represent advanced stages of intervention, emphasizing the need for timely management strategies.
Impact of APKD on Quality of Life


The impact of autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) on quality of life is a critical aspect that deserves thorough exploration. Individuals diagnosed with APKD often face a range of physical, emotional, and financial challenges. Understanding these factors is essential for healthcare providers and support systems. The insights gained can lead to improved care strategies and better support for those affected by this condition.
Psychosocial Dimensions
Living with APKD can significantly affect an individual’s psychosocial health. Patients may experience anxiety and depression due to the unpredictable nature of the disease. This emotional burden can stem from fear of disease progression and the potential need for renal replacement therapy, such as dialysis or transplantation.
Social interactions can also be impacted. Patients might withdraw from social activities due to physical limitations or fear of being judged by others. Such behavior can lead to feelings of isolation, compounding the psychological stress. Support networks—both familial and communal—are vital in navigating these complexities.
It is important to encourage open discussions about these emotional aspects. Healthcare providers can play a role by facilitating access to mental health services and support groups, creating a more holistic approach to managing the disease.
Economic Burden
The economic burden associated with APKD is another significant factor affecting quality of life. Costs arise from frequent medical visits, diagnostic tests, and necessary treatments. According to various studies, patients with APKD may face considerable out-of-pocket expenses for medications and specialist consultations.
Furthermore, as the disease progresses, the likelihood of requiring costly interventions such as dialysis or kidney transplantation increases. This not only adds financial stress but can also influence employment opportunities, leading to potential loss of income.
It is crucial that patients receive information about financial assistance programs and insurance coverage options. By addressing these economic concerns, healthcare professionals can help mitigate some of the stress associated with living with APKD.
"Managing the psychological and financial impacts of APKD is essential for improving the overall quality of life for patients. Every aspect, from emotional support to economic assistance, needs deliberate attention."
Emerging Research and Future Directions
The study of autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is rapidly evolving. Understanding emerging research and future directions is crucial for healthcare providers, researchers, and patients alike. This agenda not only focuses on the present gaps in knowledge regarding APKD but also anticipates future breakthroughs that can significantly enhance patient care and outcomes.
Current Clinical Trials
Rigorous clinical trials remain vital in the field of APKD research. These trials often investigate various treatment modalities to address the symptoms and complications of the disease. A few notable current trials include studies evaluating the efficacy of tolvaptan, a vasopressin receptor antagonist recognized for its role in slowing kidney cyst growth.
Participation in these trials can lead to increased understanding of both safe and effective treatment options. Patients enrolled in clinical trials gain access to the latest therapies while contributing to the larger body of knowledge on APKD. It is significant for practitioners to stay updated on these trials and refer eligible patients.
Advances in Genetic Research
Genetic research plays a fundamental role in our understanding of APKD. Recent advancements have highlighted the importance of gene editing techniques such as CRISPR. These technologies may provide potential avenues for direct intervention in the genetic mechanisms of APKD. Through deeper exploration of the PKD1 and PKD2 genes, researchers aim to pinpoint specific mutations and their roles in disease manifestation.
Moreover, developments in genomic sequencing technology allow for faster and more comprehensive genetic screening, enabling early detection of APKD in at-risk individuals. This progress could lead to potential preventative measures or more tailored therapeutic strategies for managing the disease.
Potential Therapeutic Options
The current landscape of therapeutic options for APKD is evolving. In addition to pharmacological approaches like tolvaptan, researchers are exploring other drug candidates that target specific pathways involved in cyst development. These may include new agents that inhibit cellular proliferation and fibrosis within the kidneys.
One promising area of research involves the modulation of specific signaling pathways that contribute to kidney cyst growth. Other potential therapeutic strategies might utilize immunomodulation to control the inflammatory responses associated with APKD.
Culmination and Implications
Autosomal polycystic kidney disease (APKD) presents significant challenges both for individuals affected by the condition and the healthcare systems managing their care. Understanding the implications of this disease is crucial for effectively addressing its impact on patients’ lives and healthcare resources. This conclusion synthesizes key information provided in the article and emphasizes the importance of continuous research and improved management strategies.
In-depth knowledge of APKD enhances the capability of healthcare professionals to deliver tailored interventions. This article has explored the complexity of the condition through its genetic roots, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and various management approaches, offering multiple avenues for enhancing patient care.
Summary of Key Insights
- Genetic Underpinnings: APKD is primarily caused by mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes, which affect kidney function.
- Clinical Manifestations: The disease can lead to a range of symptoms, including hypertension, abdominal pain, and renal failure.
- Diagnosis and Management: Timely diagnosis through imaging and genetic testing is essential for effective management. Conservative approaches may include lifestyle changes, while advanced stages may necessitate surgical intervention or pharmacological treatments.
- Emerging Research: Current studies are focused on identifying new therapeutic targets and improving understanding of the disease course through clinical trials.
These insights highlight the multifaceted nature of APKD and underscore the need for collaborative efforts in research and clinical practice.
Broader Healthcare Implications
APKD impacts not only the individuals diagnosed but also has broader implications for healthcare systems. Addressing a genetic condition such as APKD requires comprehensive care models that recognize the interplay between genetic factors and patient outcomes.
- Resource Allocation: As APKD often leads to severe complications requiring specialized care, healthcare systems must allocate resources effectively. Early intervention strategies may mitigate long-term costs associated with kidney failure.
- Psychosocial Considerations: The psychosocial effects can be profound, affecting mental health and quality of life. Awareness and integration of mental health support in treatment plans are essential.
- Health Education and Awareness: Increasing awareness among medical professionals and the general public about APKD can improve screening efforts, leading to earlier diagnosis and enhanced patient outcomes.
Adopting a proactive approach to managing APKD fosters not only better individual health outcomes but also optimizes the functioning of healthcare systems overall.















