Phrenic Nerve and Its Role in Shoulder Pain Relief

Intro
The phrenic nerve plays a critical role in the body’s neuromuscular system, primarily facilitating diaphragm movement for breathing. However, its influence extends beyond respiration. There is an intricate relationship between the phrenic nerve and shoulder pain relief, often overlooked in common discussions about pain management.
Shoulder pain can stem from various sources, including injuries, nerve compressions, or underlying medical conditions. Surprising to many, irritation of the phrenic nerve can also lead to significant discomfort in the shoulder region. Understanding this connection is fundamental for students, educators, and healthcare professionals who seek to comprehend the complexities of human anatomy and pain mechanisms.
This article aims to provide a cohesive exploration of the phrenic nerve's anatomy, its physiological functions, and its role in shoulder pain, alongside effective treatment options. The goal is to inform and educate about various factors contributing to this niche topic, fostering a comprehensive view for different audiences.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Research has shown that phrenic nerve irritation can manifest as referred pain in the shoulder area. Several studies indicate that conditions affecting this nerve, such as trauma or surgical complications, can lead to significant discomfort in seemingly unrelated areas. Understanding these findings enables clinicians to appreciate the full spectrum of pain and apply appropriate interventions.
Methodologies Employed
Studies often utilize a combination of clinical examinations and diagnostic imaging techniques to assess nerve function and pain sources. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies are common methodologies to evaluate the activity of the phrenic nerve. These methods provide insight into the nerve’s status and any potential irritations causing pain in the shoulders.
In-Depth Analysis
Detailed Examination of Results
Many scholars have noted the direct link between phrenic nerve dysfunction and shoulder pain. In cases where pain persists despite conventional treatments, further investigations into the state of the phrenic nerve become imperative. This understanding adds depth to the diagnosis and management of shoulder-related ailments.
Comparison with Previous Studies
Comparative studies reveal distinct trends in how management strategies for shoulder pain have evolved. Older methodologies often focused on localized treatments, while recent findings emphasize a more comprehensive approach that considers the role of the phrenic nerve. Consequently, this shift highlights the need for continued research in this area to refine therapeutic strategies.
"Understanding the intricate relationships between nerves and pain can lead to more effective treatment pathways."
The discussions here provide a foundation for a deeper inquiry into the phrenic nerve's impact on shoulder pain relief and encourage a multidisciplinary approach to treatment.
Prolusion to the Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve plays a pivotal role in the functionality of the diaphragm and consequently impacts respiratory and shoulder health. This section aims to highlight its crucial significance in understanding shoulder pain, revealing its multifaceted roles. Appreciating the phrenic nerve is essential for those studying or working within the realms of neurology, pain management, and physical health. It is not merely an anatomical structure; it encompasses various physiological functions that can influence shoulder pain relief.
Definition and Function
The phrenic nerve is primarily responsible for motor supply to the diaphragm, the muscle that facilitates breathing. Formed from the cervical nerve roots C3, C4, and C5, it travels from the neck down to the thoracic cavity. Its main function is to stimulate the diaphragm to contract during inhalation, thus playing a crucial part in respiratory mechanics. Besides its motor role, the phrenic nerve also carries sensory fibers from the diaphragm, central mediastinum, and parts of the pleura, making it a critical player in both motor control and sensory perception.
Anatomical Pathway
The anatomical course of the phrenic nerve is intricate. After forming in the neck, it descends vertically, crossing over the great vessels of the heart. It innervates the diaphragm, extending laterally to innervate other structures. Areas such as the pericardium and the pleura receive sensory input. Anatomical variations can exist, which can lead to differences in clinical presentations. Understanding this pathway is essential for health professionals when dealing with conditions that may cause pain and discomfort in the shoulder region.
Physiological Significance
The significance of the phrenic nerve extends beyond simple diaphragm control. Its role in pain signaling is worth noting. Irritation to the phrenic nerve can lead to referred pain in locations such as the shoulders. This suggests that issues arising in one area can have broader implications on the body's pain perception and management. Thus, a thorough understanding of its physiological functions helps in diagnosing and treating shoulder pain effectively.


"Recognition of the phrenic nerve’s impact allows a more holistic approach to shoulder pain relief."
Consideration of the phrenic nerve in therapeutic practices can consequently enhance outcomes in shoulder pain management. Ignoring its relevance may lead to oversights in treatment plans.
Shoulder Pain: An Overview
Understanding shoulder pain is crucial, especially when discussing its potential links with the phrenic nerve. The shoulder joint is complex, made up of bones, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. It provides a wide range of motion but is susceptible to various types of injuries and pains. Thus, recognizing the nuances of shoulder pain remains critical for effective treatment.
Types of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain can be broadly categorized based on its origin. Common types include:
- Acute pain: This often results from sudden injuries, such as fractures or dislocations.
- Chronic pain: Often linked to conditions like arthritis or tendinitis, this pain develops gradually and persists over time.
- Referred pain: Pain originating from other areas of the body but felt in the shoulder, such as issues related to the phrenic nerve or organs in the abdomen.
The classification helps in pinpointing treatment strategies while considering how different types of pain can engage and irritate the phrenic nerve, sometimes leading to further complications.
Causes of Shoulder Pain
Shoulder pain can arise from a multitude of factors. Common causes include:
- Rotator cuff injuries: Tears or tendinitis can limit motion and cause discomfort.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa sac may contribute to pain during movement.
- Frozen shoulder: This condition restricts flexibility, often accompanied by significant pain.
- Phrenic nerve irritation: Issues along the nerve's pathway, possibly stemming from trauma or underlying health problems, may lead to referred shoulder pain as well.
A comprehensive understanding of these causes supports accurate diagnosis and tailored interventions, potentially improving patient outcomes.
Detection and Diagnosis
Detecting shoulder pain involves a detailed process. Initially, a thorough medical history is gathered, commonly assessed with:
- Physical examinations: A healthcare provider will assess for tenderness, muscle strength, and range of motion.
- Imaging tests: X-rays or MRIs may be deployed to visualize bone structure or soft tissue problems.
- Electromyography (EMG): In cases where nerve involvement is suspected, this test evaluates the electrical activity of muscles, confirming potential phrenic nerve involvement.
Accurate diagnosis of shoulder problems connected to the phrenic nerve is vital. It not only improves treatment efficacy but also enhances an understanding of the broader implications of nerve irritation in shoulder pain management.
Intersection of Phrenic Nerve and Shoulder Pain
The relationship between the phrenic nerve and shoulder pain is often overlooked, yet it holds significant importance in the realm of pain management and treatment strategies. Understanding how the phrenic nerve interacts with shoulder pain can lead to more effective relief techniques and improved patient outcomes. It underscores the need for awareness among healthcare professionals, patients, and researchers alike.
The phrenic nerve, primarily known for its role in diaphragmatic function and breathing, also transmits pain signals that can refer to the shoulder area. This overlap can lead to misdiagnosis or misunderstanding of shoulder pain's origins. Recognizing the intersection of these two areas allows for more targeted and effective therapeutic approaches.
Mechanisms of Pain Transmission
Pain transmission related to the phrenic nerve involves several complex processes. Neural pathways from the cervical nerves, primarily C3, C4, and C5, contribute to this phenomenon. These nerves not only innervate the diaphragm but also share pathways with those that supply the shoulder region.
When an irritant stimulates the diaphragm or surrounding areas, the phrenic nerve sends signals to the brain, which may misinterpret these signals as originating from the shoulder. This type of referred pain often confuses both patients and practitioners, making accurate diagnosis critical.
Using imaging techniques, such as MRI or ultrasound, may help in identifying the actual source of pain. However, understanding the anatomical and functional aspects of the phrenic nerve can guide practitioners in making more informed decisions about the origin of shoulder discomfort.
Irritation of the Phrenic Nerve
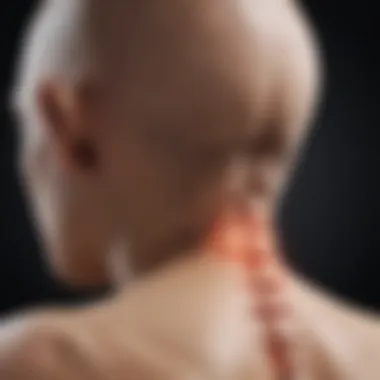

Irritation of the phrenic nerve can arise from various sources, including surgical intervention, trauma, or underlying medical conditions. Such irritation may manifest as sharp or persistent shoulder pain due to the nerve's unique role in pain signaling. Conditions like pneumonia or referred pain from intra-abdominal issues can also lead to phrenic nerve irritation, causing confusion in clinical assessments.
Symptoms can vary, but often include not only localized shoulder pain but also symptoms such as difficulty in breathing or sensations that may radiate to other areas like the neck or back. Understanding these linking pathways can aid in diagnosing and tailoring treatment for patients experiencing shoulder pain linked to phrenic nerve issues.
In summary, grasping the intersection of the phrenic nerve and shoulder pain enhances treatment modalities and improves patient outcomes. A multidisciplinary approach involving physical therapy, pharmacological interventions, and potential surgical options can provide much-needed relief.
Techniques for Shoulder Pain Relief
Understanding techniques for shoulder pain relief is critical for effective management. These methods not only address the symptoms of pain but also target its underlying causes. In this section, we will examine various strategies that encompass physical therapy, medications, alternative therapies, and invasive procedures, offering a well-rounded approach to pain management.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in shoulder pain relief. Therapists assess the patient's condition and tailor rehabilitation programs to their specific needs. Exercises often focus on strengthening the shoulder muscles, increasing flexibility, and improving posture. This proactive approach can prevent future pain episodes.
Benefits of physical therapy include:
- Personalized treatment plans
- Gradual improvement of physical function
- Education on pain management strategies
Considerations include the patient's commitment to following through with prescribed exercises.
Medications
Medications can be a useful option for alleviating shoulder pain. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce discomfort and inflammation. In more severe cases, a healthcare provider might prescribe stronger medications.
Options commonly include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Muscle relaxants
- Corticosteroid injections
While medications may offer quick relief, they should be used judiciously under a doctor's guidance. This is to avoid potential side effects or dependency.
Alternative Therapies
Exploring alternative therapies can also support shoulder pain relief. These methods often focus on holistic wellness and may include practices like acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and massage therapy.
The advantages are often linked to the potential for:
- Reducing dependence on medications
- Addressing emotional stress that contributes to pain
- Improving overall well-being
Patients interested in these options should consult with their healthcare providers to ensure they are suitable based on individual health circumstances.
Invasive Procedures
Invasive procedures are generally considered when other methods fail. Options such as joint injections or minimally invasive surgeries may provide significant relief. These procedures aim to directly address underlying issues causing pain.
Common types include:
- Arthroscopy for repairing damaged tissues
- Cortisone injections for inflammation reduction
- Phrenic nerve blockade for cases linked to nerve injury
As with all treatments, potential risks and benefits should be thoroughly discussed with a medical professional prior to proceeding.
Phrenic Nerve Block: A Treatment Option
The role of the phrenic nerve block in managing shoulder pain is a compelling topic within pain management. Phrenic nerve blocks targets the phrenic nerve, which plays a significant role in transmitting sensations related to pain and discomfort. When shoulder pain is associated with irritation of this nerve, blockading its function can provide notable relief. This procedure is particularly appealing for patients who have not found success with conventional therapies. It can be a less invasive alternative that warrants minimal recovery time while effectively diminishing pain signals.
Indications for Phrenic Nerve Block
Identifying the right candidates for a phrenic nerve block is crucial for its success. The typical indications include:
- Chronic shoulder pain due to nerve irritation or inflammation.
- Diagnostic purposes to confirm the phrenic nerve involvement in specific cases, helping distinguish between potential shoulder pathologies.
- Post-surgical pain relief for those who have undergone procedures involving exposure of the phrenic nerve.
Patients with conditions like brachial plexus neuropathy or referred pain from the diaphragm may also benefit from this procedure. Discussing these indications with healthcare professionals ensures a personalized approach tailored to individual pain origins.
Procedure Overview


The phrenic nerve block procedure is relatively straightforward but should always be performed by a trained clinician. It typically involves:
- Preparation: The patient is positioned comfortably, usually sitting upright or semi-reclined.
- Anesthesia: A local anesthetic is administered to numb the skin in the injection area.
- Ultrasound Guidance: Utilizing ultrasound technology enhances accuracy in locating the phrenic nerve.
- Injection: A needle is gently inserted to deliver anesthetic agents or cortisone around the nerve.
- Post-Procedure Care: Monitoring the patient briefly before discharge, ensuring they understand any aftercare instructions.
This block can result in immediate and sometimes prolonged relief of pain, depending on individual circumstances and pathology.
Efficacy and Outcomes
The efficacy of a phrenic nerve block can vary among patients, but many report significant improvement in pain levels. Studies suggest that:
- Immediate Pain Relief: Many individuals experience reducition in pain sensations shortly after the block is administered.
- Extended Relief: Depending on the anesthetic used and individual response, relief can last days or even weeks.
- Improved Functionality: Patients often note enhanced range of motion and ability to engage in daily activities post-procedure.
While not all patients will find complete relief, the block may allow individuals to explore other therapeutic options without the constant burden of pain.
Phrenic nerve block shows promise as a minimally invasive method for alleviating shoulder pain linked to nerve issues.
Future Directions in Research
The study of the phrenic nerve and its relationship with shoulder pain presents multiple avenues for research. Understanding these future directions is crucial for enhancing treatment modalities and improving patient outcomes. By exploring innovative therapeutic approaches and examining the neurological mechanisms of pain, researchers can provide valuable insights into effective pain management strategies.
Innovative Therapeutic Approaches
Emerging therapies offer promising routes for addressing shoulder pain linked to phrenic nerve dysfunction. These approaches include:
- Biologic Therapies: Utilizing substances derived from the body, such as platelet-rich plasma, can potentially promote healing in affected tissues.
- Regenerative Medicine: This field, which combines advanced stem cell therapies with traditional methods, aims to repair damaged nerve pathways.
- Neurostimulation: Techniques like transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and spinal cord stimulation may disrupt pain signals before they reach the brain.
These techniques not only target pain relief but also focus on the underlying causes of pain, providing a more holistic approach to treatment.
Neurological Pain Mechanisms
A deeper understanding of the neurological mechanisms behind pain will further inform treatment strategies. Researchers are currently investigating:
- Pain Pathways: How signals from the phrenic nerve contribute to the sensation of pain in the shoulder and surrounding areas. This includes studying the trigeminal nerve’s connection, as it can relate to referred pain patterns.
- Central Sensitization: This phenomenon describes a state where the central nervous system becomes hyper-responsive. This can complicate pain management, as it may prolong and intensify pain experiences.
- Psychosomatic Factors: Exploring the interplay between psychological well-being and pain perception can lead to more comprehensive therapeutic strategies.
Research in these areas will provide a solid foundation for developing effective treatment protocols and understanding patient responses to various interventions.
"Advancements in the understanding of neurological mechanisms have the potential to revolutionize pain management strategies."
In summary, future research into the phrenic nerve's role in shoulder pain presents crucial opportunities for improved medical practices. The combination of innovative therapeutic approaches and a comprehensive understanding of pain mechanisms will lead to better diagnosis and treatment of shoulder pain for many patients.
Culmination
Understanding the phrenic nerve's role in shoulder pain relief is essential in the field of pain management. The intricate connection between the phrenic nerve and the sensory pathways of shoulder discomfort reveals much about the underlying mechanisms of pain. This knowledge is significant for students, educators, and medical professionals alike, who aim to enhance their practice in treating patients.
Summary of Insights
The phrenic nerve is not merely a conduit for signals; it plays a pivotal role in mediating pain that can occur in the shoulder region. By synthesizing insights related to the anatomical and physiological aspects discussed, we can appreciate how irritation or injury to this nerve may manifest as shoulder pain. Patients often experience referred pain, wherein discomfort in the shoulder may actually stem from issues within the diaphragm or other thoracic structures.
Effective pain management strategies that incorporate an understanding of the phrenic nerve include both traditional methods and innovative therapies. In addition, the exploration of phrenic nerve block procedures has demonstrated potential benefits for those suffering from chronic shoulder pain.
Implications for Practice
The findings discussed in this article have several implications for clinical practice. By integrating knowledge about the phrenic nerve into their treatment plans, practitioners can offer more comprehensive care.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: Improved understanding aids in differentiating between various pain origins, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Tailored Treatment: Applying insight into nerve involvement allows for customized therapies, enhancing efficacy and reducing recovery times.
- Future Innovations: Continual research into the neurological underpinnings of pain may yield novel therapeutic methods.















